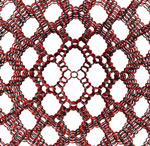
Professor Michael Deem's team calculates that there are 2.7 million possible structures.
"The asbestos-related disease in Libby is far more aggressive and rapidly progressive than what's seen in most asbestos-exposed workers," said Dr. Levin.
Study says declines follow lower application rates and EPA regulatory action over the period 1996 to 2006.
A price on carbon will increase incentives for efficiency and innovation, according to nearly all of the 144 economists who responded to NYU's Institute for Policy Integrity survey.
Over the next four months, manufacturers will test 67 chemicals using a battery of scientific assays and test guidelines from EPA.
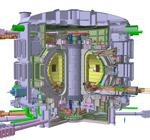
The first commercially-viable Tokamak fusion facility is using coconut-shell charcoal as an absorption mechanism.
NOAA research grants to help answer when, where and how hypoxia develops at finer temporal and spatial scales.
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences gathered scientists on Oct. 6 to begin an integrated research initiative that will enable a comprehensive assessment of possible health effects.

Sandia Laboratory and others will study microbial genes in arid grasslands.
Scientists in Switzerland say up to 35 percent of the total nanosilver in tested fabrics was released, mostly in the first wash.
USGS report credits efficiency, technology for lower water usage results.
Scientists can use it to study permeable surfaces that will stem the flow of stormwater into waterways
SETI Institute and NASA are using a Zeppelin over San Francisco Bay to gather data for a predictive model of microbial ecosystem change.
Scientists can use it to study permeable surfaces that will stem the flow of stormwater into waterways
Researchers identified offshore sand sources that could be used for future beach replenishment without causing a bigger erosion problem elsewhere, a USGS lead scientist says.
Although one critic says the model's sea level rise and subsidence rates were optimistic, he admits the model still predicts land could be delivered to the sinking delta.
Carbon nanotubes have enabled the chemical engineers to achieve hydrogen storage capacity up to 8 percent by weight.
Researchers are studying the genomes of uncultivated microbes found in OMZs to better understand how they participate in global geochemical cycles such as the carbon and nitrogen cycles.
Proposals must be submitted by Nov. 23 and all work must be completed by April 2010.