Researchers tested taxi drivers before, during, and after the 2008 Beijing Olympics for their heart rate variability in response to varying levels of particulate matter pollution.
Temperature and photosynthetic active radiation are the most important variables in determining what future forests might look like, according to the study.
Molecules containing several fluorine atoms tend to be strong greenhouse gases, compared to molecules containing chlorine and/or hydrogen.
X-ray absorption spectroscopy helps researchers quantify the rate of reaction between contaminants and soil and water.

U.S. Geological Survey study notes abundance of eelgrass keeping the Pacific brant from migrating to Mexico.
Researchers claim the light-to-electricity conversion is very efficient but scaling up the device would be challenging.
Hawaii timber plantations actually use more water than native forests, which may place ecosystems and people at high risk for water shortages.
A University of Michigan study found an 11 percent reduction in energy demand per person since 1960.
Professor Norman Pace sampled showerheads in seven states to find Mycobacterium avium.
Study suggests additional research is needed to determine if these fluorochemicals could be harmful.
Scientists in China treated cucumber plants with a plant hormone and various pesticides and found lower levels of residues in the plants.
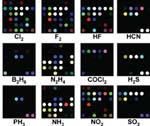
Kenneth S. Suslick and colleagues have developed an optoelectronic nose for the detection of toxic industrial chemicals.
EPA-NIEHS study found that an increase of 1 ppm carbon monoxide in the maximum daily one-hour exposure is linked to a 0.96 percent increase in the risk of hospitalization from cardiovascular disease for people 65 years and older.
The alarmist comments presented in the following article from your newsletter are very irresponsible given recent information that has come to light regarding the fact that global cooling has actually taken place over the past ten years.
If efforts to lower greenhouse gases are not successful, governments may turn to geoengineering techniques, which have not been studied or found to be effective at an affordable cost.
University of Utah chemists have developed a method to detect if drinking water aboard the International Space Station is adequately disinfected.
N-ST*R tests mineralizable soil nitrogen, enabling farmers to better calculate the amount of nitrogen that should be applied to rice crops for maximum yield but no excess that might be carried away as runoff.
Tapping Bigleaf maples, which generate a steady voltage of up to a few hundred millivolts, University of Washington researchers developed a boost converter and used the stored power to operate low-power sensors.